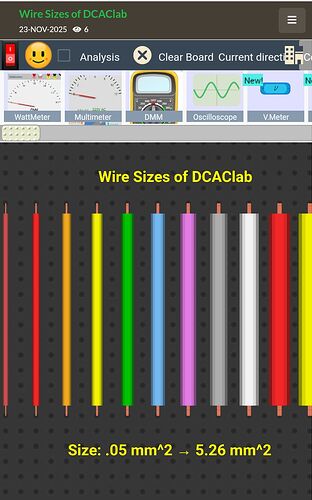
Wire Area Size in DCAClab Circuit Simulator & Burning Effect by Current
1. What you see in DCAClab UI
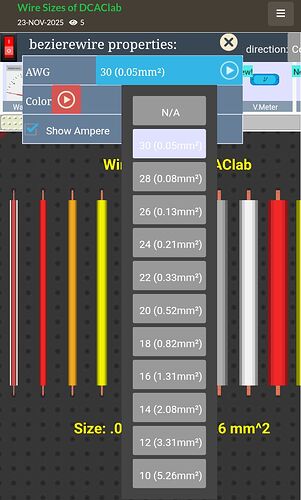
In the DCAClab Circuit Simulator, the wire uses a Wire Properties of DCAClab panel where you can configure:
- AWG (American Wire Gauge) size
- Wire Color
- Show Ampere (Enable / Disable current display)
The AWG dropdown includes the following sizes:
- 30 (0.05 mm²)
- 28 (0.08 mm²)
- 26 (0.13 mm²)
- 24 (0.21 mm²)
- 22 (0.33 mm²)
- 20 (0.52 mm²)
- 18 (0.82 mm²)
- 16 (1.31 mm²)
- 14 (2.08 mm²)
- 12 (3.31 mm²)
- 10 (5.26 mm²)
2. AWG to Area Mapping (As used in DCAClab)
| AWG | Cross-sectional Area (mm²) |
|---|---|
| 30 | 0.05 |
| 28 | 0.08 |
| 26 | 0.13 |
| 24 | 0.21 |
| 22 | 0.33 |
| 20 | 0.52 |
| 18 | 0.82 |
| 16 | 1.31 |
| 14 | 2.08 |
| 12 | 3.31 |
| 10 | 5.26 |
3. Why wires burn in DCAClab
Wire burning happens when excessive current flows through a wire that cannot dissipate heat fast enough.
Relevant Physics:
Resistance of a wire:
R = ρ × L / A
Power converted into heat:
P = I² × R
Where:
R = Resistance (Ohm)
ρ = Resistivity of copper = 1.68 × 10⁻⁸ Ω·m
L = Length of wire (meter)
A = Cross-sectional area (m²)
I = Current (Ampere)
More current → more heat → insulation melts → wire burns.
4. Practical Calculation Examples
Example 1: AWG 30 (0.05 mm²)
Area conversion:
0.05 mm² = 5.0 × 10⁻⁸ m²
Resistance per meter:
R = (1.68 × 10⁻⁸) / (5.0 × 10⁻⁸) = 0.336 Ohm/m
Power dissipation:
At 1A:
P = 1² × 0.336 = 0.336 W per meter
At 2.5 A:
P = 2.5² × 0.336 = 6.25 × 0.336 = 2.10 W per mete
Result: The Wire (0.05 mm²) is burned through current (2.5 A).
Example 2: AWG 10 (5.26 mm²)
Area conversion:
5.26 mm² = 5.26 × 10⁻⁶ m²
Resistance per meter:
R = (1.68 × 10⁻⁸) / (5.26 × 10⁻⁶) = 0.00319 Ohm/m
At 20A:
P = 20² × 0.00319 = 400 × 0.00319 = 2.28 W per meter
Result: The Wire (5.26 mm²) won’t be burned through current (20 A).
Resistance Per Meter of the all wires:
- 30 (0.05 mm²) ➝ 0.337 Ω/m
- 28 (0.08 mm²) ➝ 0.212 Ω/m
- 26 (0.13 mm²) ➝ 0.133 Ω/m
- 24 (0.21 mm²) ➝ 0.084 Ω/m
- 22 (0.33 mm²) ➝ 0.053 Ω/m
- 20 (0.52 mm²) ➝ 0.033 Ω/m
- 18 (0.82 mm²) ➝ 0.021 Ω/m
- 16 (1.31 mm²) ➝ 0.013 Ω/m
- 14 (2.08 mm²) ➝ 0.008 Ω/m
- 12 (3.31 mm²) ➝ 0.005 Ω/m
- 10 (5.26 mm²) ➝ 0.003 Ω/m
5. Approximate Safe Current (DCACLab)
| AWG | Area (mm²) | Safe Continuous Current |
|---|---|---|
| 30 | 0.05 | 1 - 2.2 A |
| 28 | 0.08 | 1 - 2.8 A |
| 26 | 0.13 | 1 - 3.5 A |
| 24 | 0.21 | 1 - 4.4 A |
| 22 | 0.33 | 1 - 5.6 A |
| 20 | 0.52 | 1 - 7.1 A |
| 18 | 0.82 | 1 - 8.9 A |
| 16 | 1.31 | 1 - 11.3 A |
| 14 | 2.08 | 1 - 14.2 A |
| 12 | 3.31 | 1 - 17.9 A |
| 10 | 5.26 | 1 - 22.5 A |
If current exceeds these levels, DCAClab visually shows wire burning.
6. How to Test Burning in DCAClab
- Select the wire.
- Open Wire Properties panel.
- Choose AWG size.
- Enable Show Ampere.
- Apply voltage source.
- Gradually increase current.
- Observe.
- Wire color change
- Heating indicator
- Burning animation effect
7. Why Thin Wires Burn Faster
- Smaller cross-sectional area
- Higher resistance
- Higher resistance + High current = Excessive heat
- Heat exceeds insulation tolerance → Wire burns
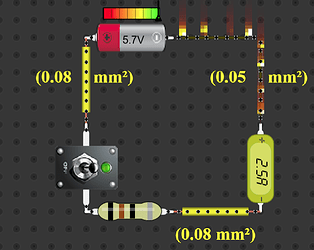
8. Practical Demo Scenario
Wire: AWG 30
Length: 0.5 meter
Voltage: 5V
Resistance:
R = 0.336 × 0.5 = 0.168 Ohm
Current if no load:
I = V / R = 5 / 0.168 = 29.7 A
Result: Instant wire burn
Solution:
- Add series resistor
- OR use thicker wire such as AWG 16 or below
9. Best Practice for DCAClab
- Always use resistor or proper load
- Avoid direct short circuits
- Monitor Ampere display
- Keep current below 80% of safe limit
- Use thicker wire for high current circuits
10. Conclusion
DCAClab wire simulation realistically models:
- AWG size vs Resistance
- Current flow visualization
- Thermal burning behavior
- Real-time Ampere monitoring
Understanding the relationship between AWG, current, resistance, and power helps you design safer and more accurate circuit simulations in DCAClab.